Flow
control
We have applied this approach to the destruction of tip vortices produced in the wakes of aircraft and to drag reduction in three-dimensional cylinder wakes.
We also use penalization methods to simulate flows around obstacles and analyze passive control methods based on porous coatings.
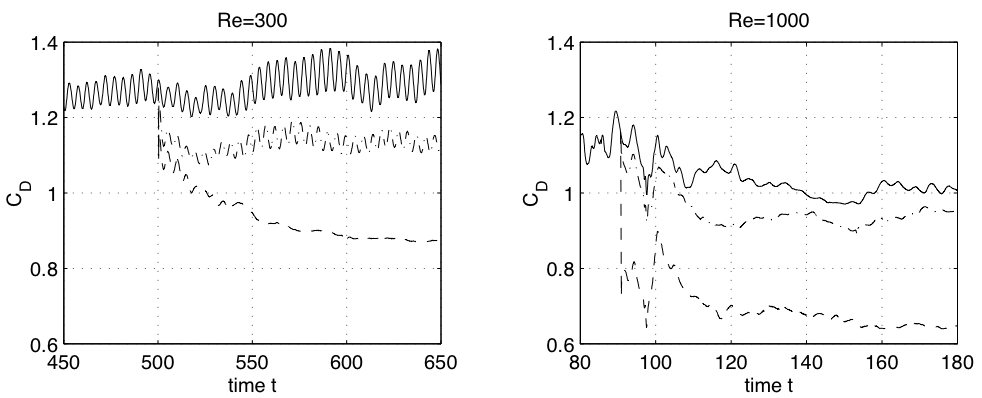 |
 |
| 3D
(dash) vs 2D (dash-dot) optimal drag reduction in a cylinder wake for
two values of the Reynolds number. Solid line is the uncontrolled drag. |
Cylinder
controlled wake for optimal drag reduction (video) |
[1]
G.-H. Cottet,
I. Sbalzarini,
S. Muller and P. Koumoutsakos, Optimization
of trailing vortices by
Evolution Strategies, Center for Turbulence Research,
Proceedings
of the Summer Program, 2000. pdf file
[2] G.-H. Cottet
and P. Poncet, Simulation and
control of
three-dimensional wakes,
Computers and fluids, 33, 97-713, 2004. pdf file
[3] P. Poncet, G.-H. Cottet and P. Koumoutsakos, Control of three-dimensional wakes using evolution strategies, C. R. Mecanique 333 (2005), 65-77, 2005. pdf file
[4] P. Poncet, R. Hildebrand, G.-H. Cottet and P. Koumoutsakos, Spatially distributed control for optimal drag reduction of the flow past a circular cylinder, J. Fluid Mech., 599, 111-120, 2008. pdf file
[5] C. Mimeau, I. Mortazavi and G.-H. Cottet , Passive flow control around a semi-circular cylinder using porous coatings, International Journal of Flow Control, 6, 43-50, 2014. pdf file
[6] C. Mimeau, G.-H. Cottet and I. Mortazavi Direct numerical simulations of three-dimensional flows past obstacles with a vortex penalization method, Computers and Fluids (2016), pp. 331-347. pdf
file
[7] C. Mimeau, I. Mortazavi and G.-H. Cottet Passive control of the flow around a hemisphere using porous media, to appear in European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 2017. pdf
file
